Short term variation Analysis versus Visual Evaluation of cardiotocography in Fetal Growth Restriction (SAVE FGR)
For patients
In managing early-onset fetal growth restriction (eoFGR), we use cardiotocography (CTG; the heart rate monitor of the baby) to monitor the health of the baby. If the baby’s heart rate shows signs of low oxygen levels, birth is expedited, usually with a caesarean section. Caregivers can check the aspects of the heart rate monitor visually or with computer software.
The SAVE FGR study looks at which method is better for babies with eoFGR: visual evaluation alone or visual evaluation with software help. We will collect heart rate data using patches on the abdomen and monitors from NEMO Healthcare or the regular Doppler probes on the abdomen.
In the first part of the study, all centers will only do visual checks using their standard system. At set times, centers will switch to the second part of the study. In this part, they will use both visual checks and software analysis. If the software analysis shows that the variability of the fetal heart rate is below the thresholds, the clinician will be advised to expedite the birth.
For professionals
In the management of early-onset fetal growth restriction (eoFGR), cardiotocography (CTG) is used for fetal monitoring. If the fetal heart rate pattern shows changes that could indicate chronic or acute fetal hypoxia, birth (usually with caesarean section) is expedited. The most important aspects that indicate hypoxia are repeated spontaneous decelerations and reduced variability. Heart rate variability can be assessed visually by the caregiver or quantified by computer software.
The SAVE FGR multicentre stepped-wedge cluster-randomized study investigates which approach leads to better outcomes for fetuses with eoFGR: visual assessment alone or visual assessment, supported by software-quantification of heart rate variability. Fetal heart rate will be collected with abdominal adhesive patches and fECG monitors from our study partner NEMO Healthcare. The fallback method is conventional CTG with Doppler probe.
In the first ‘control’ part of the study, all centers will only assess CTGs visually with the use of their standard central monitoring system. At fixed times, determined by cluster-randomization, centers will switch to the intervention’ period. In this second period of the study, in addition to visual assessment, the clinicians will use software-quantified variability. The monitoring system MOSOS of our partner ICT HCTS will be used that has the original Daws and Redman criteria built in. Below the TRUFFLE defined thresholds of variability the clinician is advised to expedite birth.
Read more
A secondary study aim is to collect as many prognostic factors for outcomes as possible, in order to further optimize the monitoring-delivery strategy and improve outcomes, in the overarching FGR PODS. This explains some of the elaborate study procedures and underwrites their importance. This includes the biobanking of materials and the long-trace fetal ECG signal acquisition with the NEMO application. The end goal is to develop advanced and integrated decision support for the clinicians.
Flowchart SAVE FGR
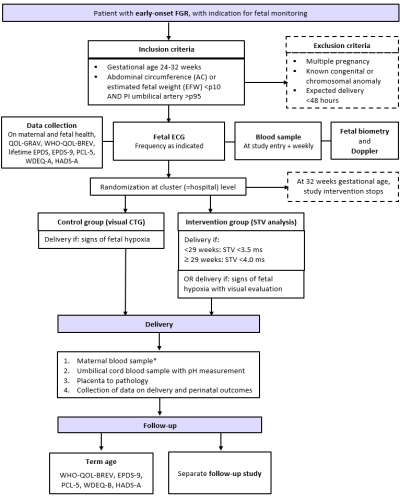
Who can participate?
Patients with a pregnancy complicated by eoFGR, who are intensively monitored with the intent to time delivery can participate if they match the inclusion criteria (and do not fulfil exclusion criteria). Usually, patients are hospitalized.
Inclusion criteria:
- Gestational age 24-32 weeks.
- Starting from thresholds of viability, once active management is agreed upon
- Singleton pregnancy
- FGR based on likely placental insufficiency
- AC and/or EFW <p10 in combination with UA PI >p95
Exclusion criteria:
- Congenital anomalies or known chromosomal anomalies affecting relevant outcomes
- Maternal indication for birth within 48 hours (pre-eclampsia without need for immediate delivery can be included)
- Maternal age <18
- Not capable to understand the information
- Not fluent in English, Danish, French, Dutch
Read more
The patient information sheet can be found in your hospital’s research folder.
Before the study
- Install stand-alone MOSOS CTG for STV evaluation and NEMO hardware
- e-learning and hands-on training of peer front runners for application of NEMO patches and equipment handling
- Arrange biobanking logistics
- Arrange with Pathology about options for storage of paraffin blocks, scanning of histologic slides; use of free-of-charge Synoptic Reporting Tool for reporting of histology findings.
What needs to be done, by who?
By the clinical team
- Inform patient and secure informed consent
- Inform patients about study website which will provide information for patients about eoFGR and the study project
- Inform patients of their unique study ID, prepare them for prompted questionnaires (distributed by central team)
- At inclusion and weekly thereafter venipuncture with 1 tube 10 mL EDTA, 1 tube 10 mL serum tube, preferably at scheduled venipuncture moments.
- Send tubes to lab for -70/80oC storage of plasma and serum.
- Apply the NEMO patch morning to evening and follow instructions
Read more
- The CTG is evaluated and acted upon as per standard clinical protocol
- [In the intervention period] Follow instructions twice daily (or as many times as clinically indicated) to calculate short term variation.
- If STV is <3.5 ms below 29 weeks or <4.0 ms at 29 weeks and later, the clinician is advised to expedite delivery, also in the absence of repeated decelerations.
After delivery
- Umbilical cord blood sampling for biobank. Use venous blood in plasma tube (EDTA). Usually in combination with pH measurement.
- Placenta to pathology.
By the local research team
- Enter pseudonymised patient data in the secure trial data platform (Castor, link on study website immediately at inclusion
- Report patient ID in medical file
- Inform local clinical staff of study procedures, address any concerns, oversee study procedures
- Record process data and outcome data in the CASTOR secure trial data platform
- Ensure data storage of fECG signals
- Upload coded data files of fECG tracings to secure data platform (Amsterdam UMC)
- Arrange sending biobanking materials at agreed time points
- Contact patients when necessary
By the central study team
- Send out questionnaires at given time points
- Within 2 days after inclusion in study: general information, EPDS, GRAVQoL
- At 1M, 6M, 12M post term date questionnaire regarding mother & infant hospital data, infant growth, EDS, GRAVQoL
- At 2 questionnaire regarding mother & infant hospital data, infant growth, EDS, GRAVQoL, ASQ.
- Oversee progress of data and material acquisition
- Provide (updated) information on study website
- Monthly newsletter to local teams, quarterly newsletter to patients (who wish)
For more detailed, please check our practical protocol.



